
ILASS Europe, 33rd Conference on Liquid Atomization & Spray Systems, Lund, Sweden, 2025
Machine learning approach to determine the suspension concentration
In this study, the light scattering of a colloid droplet on an elliptical Gaussian beam was analyzed to determine the concentration of the suspended particles in a suspension droplet. The light scattering was studied for a fixed scattering angle in the backscatter region. The data was acquired with a high time resolution by using photo multiplier and high-speed signal analyzer. The measurements of the different suspension concentrations of the droplet were performed in order to provide the sufficient data for the construction of an empirical model giving the correlation between the light scattering signal and the suspension concentration. The measurements were carried out with a monodisperse droplet generator. The correlation between the light scattering signal and the suspension concentration in the droplet was established by two methods, relying on an artificial neural network and relying on statistical properties of the light scattering signal.

11th Int. Symposium on Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer, Tokyo, Japan, 2025
Refractive index determination of dynamic droplets in a flow by analyzing light scattering signals with a machine learning approach
In this study, we present a new method for determining the refractive index of dynamic droplets in a spray using a machine learning approach, where the four light scattering signals from individual droplets were analyzed. These light scattering signals were generated by a Time-Shift-Time-of-Flight (TSTOF) system. The spray was produced using a flat fan nozzle, and to vary the refractive index, a water-glycerin mixture with different mixing ratios was used. First, a machine learning model was developed to analyze the four light scattering signals. In addition, we explored whether the number of signals could be reduced while maintaining calculation precision.
DECHEMA Agglomerations- und Schüttguttechnik sowie Trocknungstechnik, Friedrichshafen, Deutschland, 2025
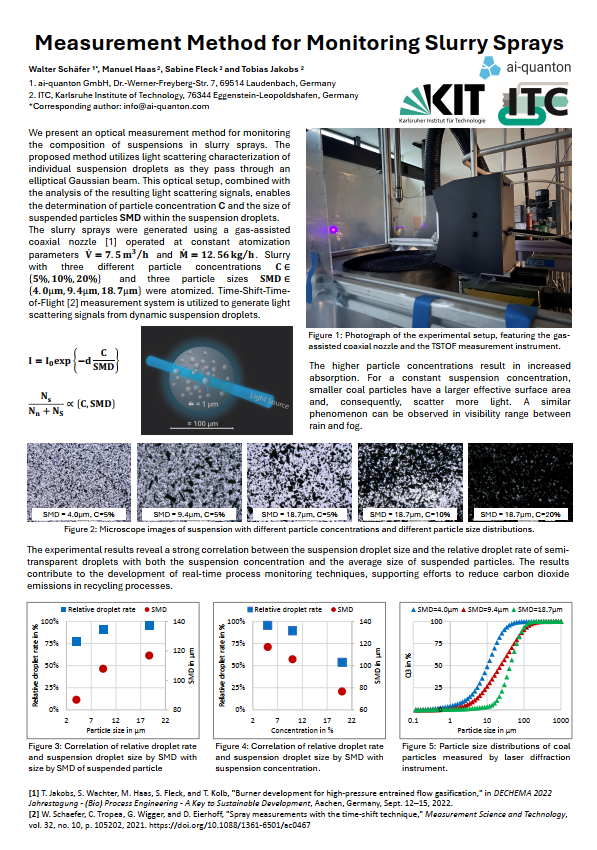
Measurement methode for monitoring slurry sprays
In this study, we present a basic idea for a robust optical measurement method for practical monitoring of slurry sprays with high mass concentrations, as typically used in combustion processes. The proposed approach is based on analyzing the transparency properties of individual dynamic droplets within the slurry spray. These so-called dynamic slurry droplets consist of a base fluid and suspended solid particles. Our method enables the determination of the mass concentration of solid particles and provides an estimate of their average size. The resolution of this technique allows for the detection of errors in the slurry mixing process, and even in the milling process of the solid particles prior to mixing. To atomize slurries with high mass concentration, an experimental setup with a gas-assisted coaxial nozzle was employed. Slurries with three different mass concentrations and three particle size distributions were tested, resulting in five combinations. Theoretical expectations and experimental results show a strong correlation, highlighting the potential of the proposed method for slurry spray monitoring. These findings contribute to the development of real-time process monitoring techniques for a wide range of suspension spray applications.

16th International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Shanghai, China, 2024
Particle characterization by analyzing light scattering signals with a machine learning approach
We present here a new instrument in combination with a machine learning approach to achieve a more cost-effective and compact measurement instrument for particle characterization in a flow based on the established measurement technique known as the Time-Shift-Time-of-Flight (TSTOF) technique. In this study, we propose a machine learning model capable of using only a single signal in this device to determine the same information about particles, such as particle size and particle velocity, traditionally obtained from the classical measurement device based on the TSTOF technique, where four signals have been used. To achieve this, we train a machine learning model using the four signals, but connect only a single signal to the model in the final step. The initial experimental results have been conducted, and preliminary calculations demonstrate high potential for this method.
36. Hofer Vliesstofftage, Hof, Deutschland, 2023
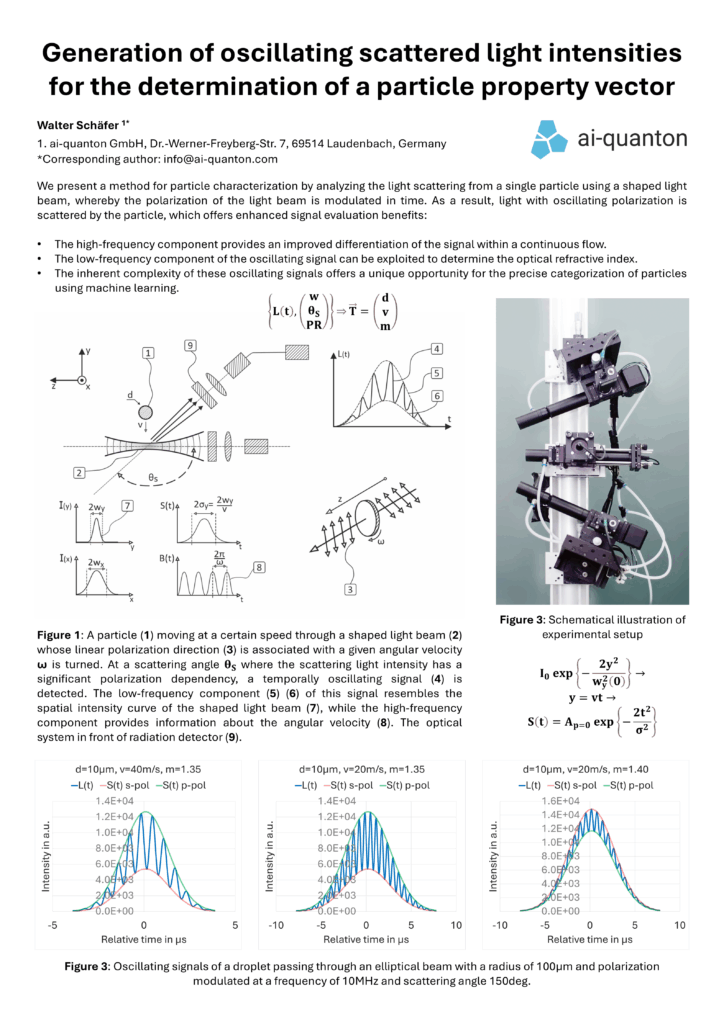
Method for the generation of oscillating scattered light intensities for the determination of a particle property vector
We present a method for particle characterization by analyzing the light scattering from a single particle using a shaped light beam, whereby the polarization of the light beam is modulated in time. As a result, light with oscillating polarization is scattered by the particle, which offers enhanced signal evaluation benefits. First, the frequency of the high-frequency component provides an improved differentiation of the signal within a continuous flow. Second, the low-frequency component of the oscillating signal can be exploited to determine the optical refractive index. Finally, the inherent complexity of these oscillating signals offers a unique opportunity for the precise categorization of particles using machine learning.
35. Hofer Vliesstofftage, Hof, Deutschland, 2022
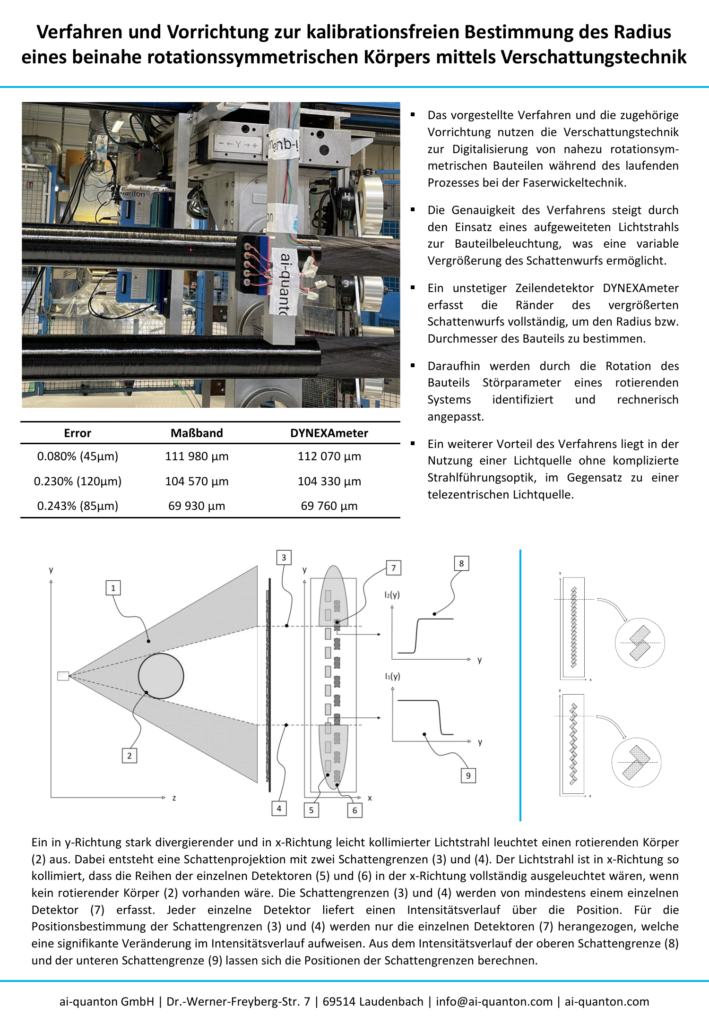
Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur kalibrationsfreien Bestimmung des Radius eines beinahe rotationssymmetrischen Körpers mittels Verschattungstechnik
Das vorgestellte Verfahren und die zugehörige Vorrichtung nutzen die Verschattungstechnik zur Digitalisierung von nahezu rotationsym-metrischen Bauteilen während des laufenden Prozesses bei der Faserwickeltechnik. Die Genauigkeit des Verfahrens steigt durch den Einsatz eines aufgeweiteten Lichtstrahls zur Bauteilbeleuchtung, was eine variable Vergrößerung des Schattenwurfs ermöglicht. Ein unstetiger Zeilendetektor DYNEXAmeter erfasst die Ränder des vergrößerten Schattenwurfs vollständig, um den Radius bzw. Durchmesser des Bauteils zu bestimmen. Daraufhin werden durch die Rotation des Bauteils Störparameter eines rotierenden Systems identifiziert und rechnerisch angepasst. Ein weiterer Vorteil des Verfahrens liegt in der Nutzung einer Lichtquelle ohne komplizierte Strahlführungsoptik, im Gegensatz zu einer telezentrischen Lichtquelle.
Measurement Science and Technology, 2021
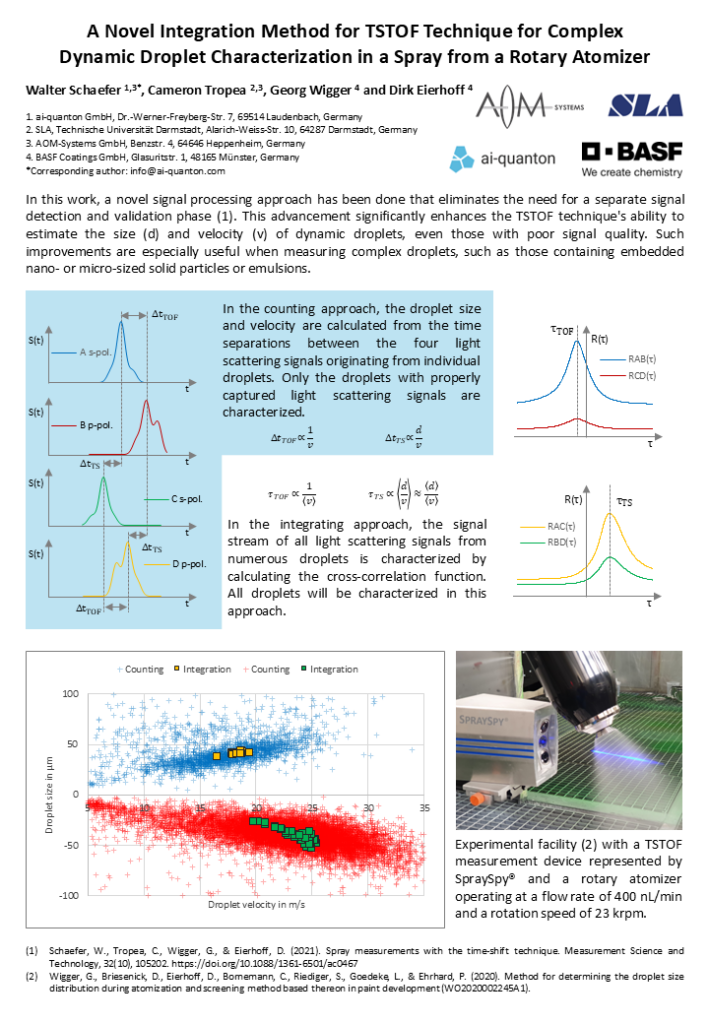
Spray measurements with the Time-Shift technique
The time-shift technique is a well-documented technique for the size and velocity measurement of individual drops passing through one or two tightly focused laser beams. It is a counting technique, nominally applicable for pure liquid drops, but with potential to also characterize drops with embedded particles or drops containing a second dispersed phase. In the present study a novel approach to signal processing is introduced in which the signal detection and validation phase is eliminated. This extends the capabilities of the time-shift technique in two manners. For one, size and velocity estimates are made possible for drops exhibiting very poor signal structure or signal-to-noise ratio. Such signals are commonly expected when measuring complex drops, either drops with embedded nano/micro-particles (dispersions) or emulsions. Second, the size and velocity distributions are estimated not by processing of signals from individual drops (single realization counting technique), but from a large ensemble of drop signals, improving both computational speed and reducing the influence of outliers in final statistics. These capabilities are achieved without sacrificing accuracy of mean and variance estimates of size and velocity of drop ensembles. To demonstrate the advantages of this new approach, measurements of a paint spray are presented, processed using both standard processing routines and the new approach. Limitations concerning the application of this new approach are discussed in detail.
